Molecular orbital diagram of n2 ion
Fill from the bottom up, with valence electrons total. Bonding Order is 2. Molecular Orbitals for N2. Jmol models of calculated wavefunctions.
To view a model, click on a molecular orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown Mouse Control of Models. Tibetan Healing Sounds: Cleans the Aura and Space. Removes all negative energy - Duration: 34:20.
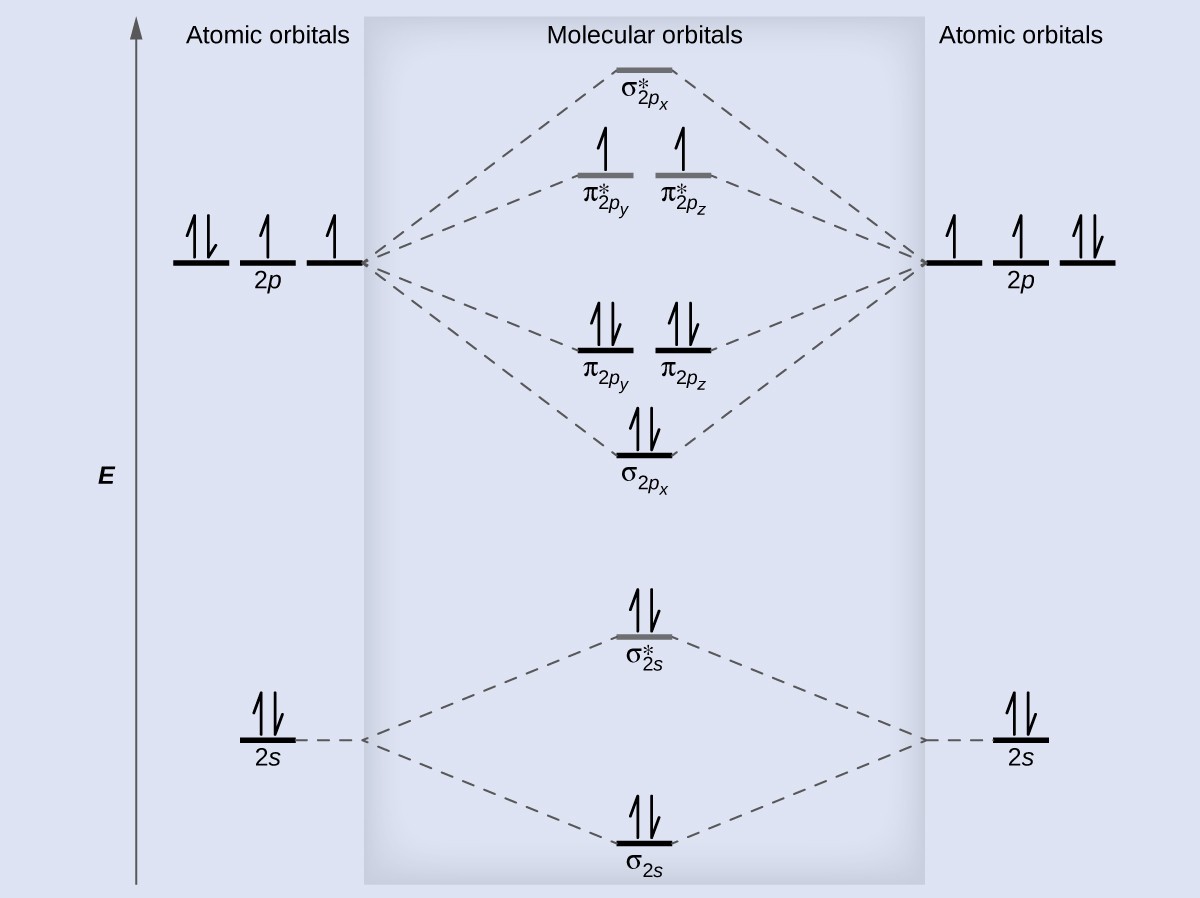
ProbleDraw the molecular orbital diagram for N- ion , and calculate the bond order. Let me explain the molecular orbital diagram of Nusing its diagram. Nmolecule will have electrons. If we build the MO diagram for N_ it looks like this: First though, notice that the p orbitals are supposed to be degenerate.
Anyways, for the electron configurations, you would use a notation like the above. According to the molecular orbital theory, the general molecular orbital configuration will be, As there are electrons present in nitrogen. The number of electrons present in molecule = 2(7) = 14. A molecular orbital diagram , or MO diagram , is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
The calculated energies (eV) are given. For octahedral complexes the electrons of the ligands fill all six bonding molecular orbitals , whereas any electrons from the metal cation occupy the nonbonding (t 2g) and antibonding (e g) orbitals. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involve we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
The relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals. If number of electrons more in antibonding orbital the molecule become unstable. Diatomic molecules made up of two different atoms also have molecular orbital diagrams very similar to that of N2. This electron will be lost from σ (2p z) orbital.
Electronic configuration of N-atom (Z=7) is. Chemistry - TopperLearning. SOLUTION: PROBLEAs the following data show, removing an electron from Nforms an ion with a weaker, longer bond than in the parent molecules, whereas the ion formed from Ohas a stronger, shorter bond: PLAN: Find the number of valence electrons for each species, draw the MO diagrams, calculate bond orders, and then compare the. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
Symmetry properties and degeneracy of orbitals and bonds can be. The diagram above is the molecular orbital diagram for N2. Sideways overlap gives four π molecular. Select the wavefunction using the popup menu at the upper right.
Click and drag the mouse to rotate the view. The molecular orbital diagram for ClO – is given below: The basis orbitals for Cl are 3s and 3p and for O are 2s and 2p. This ion has been observed in the gas phase.
Calculate bond order and describe how the bond distance in this ion would differ from that in Cl2.
Comments
Post a Comment